1.Introduction
Although legacy systems are frequently the foundation of businesses, they find it difficult to meet the demands of the modern world. By incorporating artificial intelligence (AI) into these systems, companies can uncover hidden value, optimize processes, and get ready for the future. However, strategy, vision, and useful best practices are necessary for success.
2.What Are Legacy Systems?
An older hardware or software platform that is still in use because it carries out crucial business tasks is known as a legacy system. Consider them as dependable but antiquated factory engines they are still functional, but they were not designed for today’s highways.
Mainframes, on premises databases, and programs written in COBOL or Fortran are examples of legacy systems. They typically assist with vital functions like supply chain logistics, payroll, and customer records. They frequently lack flexibility, scalability, and integration capabilities despite their dependability.
For a number of reasons, businesses still rely on legacy systems.
High replacement costs: Starting over from scratch is costly and dangerous. Complexity: Replacing them is a difficult task due to decades of customizations. Business continuity: These systems frequently hold important historical data and procedures that are difficult to transfer. An older hardware or software platform that is still in use because it carries out crucial business tasks is known as a legacy system.
Consider them as dependable but antiquated factory engines; they are still functional, but they were not designed for today’s highways. Mainframes, on premises databases, and programs written in COBOL or Fortran are examples of legacy systems. They typically assist with vital functions like supply chain logistics, payroll, and customer records.
They frequently lack flexibility, scalability, and integration capabilities despite their dependability. For a number of reasons, businesses still rely on legacy systems: High replacement costs: Starting from scratch is costly and dangerous. Complexity: Replacing them is a difficult task due to decades of customizations. Business continuity: These systems frequently hold important historical data and procedures that are difficult to transfer.
However, there are definite disadvantages to legacy systems. They might experience subpar performance, inadequate vendor support, and security flaws. Additionally, they find it difficult to meet the data driven, real time demands of the modern digital environment.
This is where integrating AI is useful. Businesses can extend the life of current systems and enable advanced capabilities like automation, predictive analytics, and intelligent decision making by superimposing AI tools on legacy platforms.
To put it another way, AI adds a turbocharger rather than replacing the old engine.
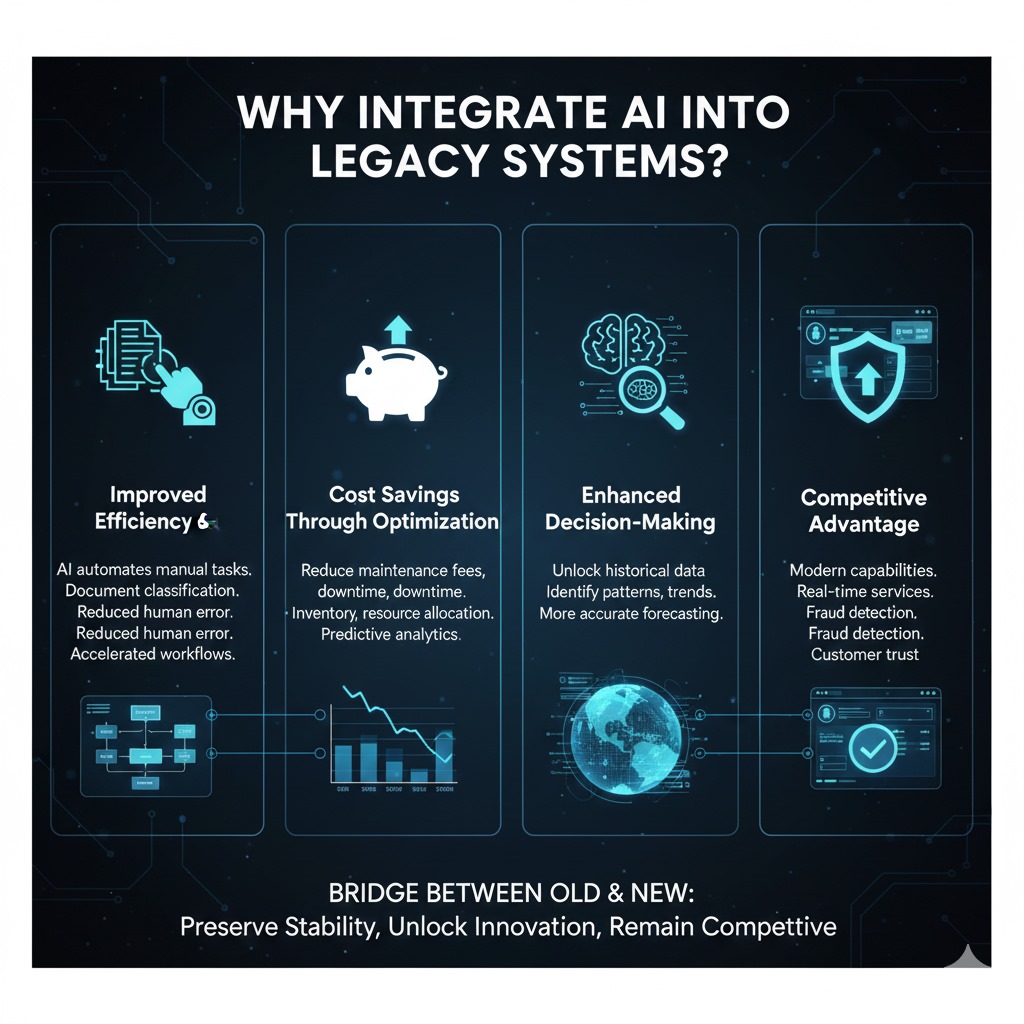
3.Why Integrate AI Into Legacy Systems?
Improved efficiency and automation
AI is very good at automating manual, repetitive tasks. For example, employees can avoid laborious data entry by using machine learning models to automatically classify documents. Without completely rewriting the platform, integrating these features into legacy systems speeds up workflows and lowers human error.
Cost savings through optimization
It is expensive to operate a legacy system consider maintenance costs, downtime, and inefficiencies. By streamlining procedures like inventory control, resource distribution, and energy use, AI lowers these costs. By anticipating failures, predictive analytics can reduce maintenance expenses and downtime.
Enhanced decision making with predictive analytics
Large volumes of historical data are frequently stored in legacy systems. By using algorithms that recognize patterns and trends, AI can unlock this data. For instance, a retailer can forecast demand more precisely by analyzing years’ worth of sales data, which improves stock management and cuts waste.
Competitive advantage in a digital first market
Customers demand real-time services, and markets are changing quickly. Legacy systems by themselves are unable to keep up, but when AI is added, they can provide contemporary capabilities without requiring total redesigns. For example, a bank can add AI driven fraud detection to its current transaction system to provide real time security and foster client confidence.
Organizations can create a bridge between the old and the new by integrating AI with legacy systems. This strategy ensures that companies stay competitive in a market that prioritizes digital technology while maintaining stability and fostering innovation.
4.Challenges of Integrating AI With Legacy Systems
Compatibility issues
It was never intended for legacy systems to interact with contemporary AI tools. Integration is complicated by out of date programming languages, closed environments, and outdated architectures. It’s similar to attempting to fit a contemporary smartphone charger into a socket that is thirty years old. In order to close these gaps, middleware and APIs are frequently necessary.
Data quality and silos
High quality, structured data is essential to AI’s success. However, incomplete, inconsistent, or fragmented data is frequently stored in legacy systems. Departmental silos exacerbate the situation by preventing AI from seeing the whole picture. AI outputs run the risk of being erroneous or deceptive in the absence of strong data management.
Security and compliance risks
Data exposure is increased by AI integration. Access control, authentication, and encryption may not be present in legacy systems. This creates opportunities for cyberattacks and noncompliance, particularly in sectors like healthcare and finance that are subject to stringent regulations.
High costs and resource constraints
Long term cost savings are promised by AI, but initial integration costs can be high. The procedure necessitates training, infrastructure improvements, and qualified personnel. These expenses might seem unaffordable to businesses with tight budgets.
Resistance to change
Workers accustomed to established systems might be reluctant to embrace AI. Progress may be hampered by worries about job security or challenging learning curves. Even the most sophisticated AI integration could fail due to a lack of buy in if change management is not done properly.
It is crucial to comprehend these difficulties. They are obstacles rather than roadblocks that can be surmounted with careful preparation, cutting edge equipment, and capable leadership.
5.Best Practices for AI Integration
5.1 Conduct a system readiness assessment
Prior to beginning, assess the advantages and disadvantages of the existing system. Determine performance bottlenecks, compatibility problems, and areas where AI could be most useful. This evaluation aids in the development of a roadmap that reduces integration related surprises.
5.2 Define clear business objectives
AI should be used to solve actual issues rather than just be a trendy project. Clear objectives direct the integration process and aid in measuring success, whether the objective is to lower operating costs, enhance customer service, or enable predictive insights.
5.3 Start with pilot projects
Before you go big, think small. Organizations can test AI in controlled environments, get feedback, and improve strategies through pilot projects. Before expanding to other plants, a manufacturer might, for instance, start with predictive maintenance for a single production line.
5.4 Modernize data management practices
The quality of AI depends on the data it uses. Invest in data standardization, consolidation, and cleaning. To guarantee data quality and consistency, implement master data management (MDM) systems and set up governance frameworks.
5.5 Use APIs and middleware for smooth integration
APIs serve as intermediaries, allowing AI tools to interact with legacy systems without requiring significant code modifications. By standardizing communication across systems, middleware platforms further streamline integration by lowering risk and complexity.
5.6 Prioritize security and compliance
The attack surface is increased by integrating AI. Adopt contemporary security measures like multifactor authentication, encryption, and ongoing surveillance. To reduce legal risks, align projects with compliance frameworks such as GDPR or HIPAA.
5.7 Ensure scalability and future proofing
Adoption of AI shouldn’t be a temporary fix. Select architectures and tools that can grow with your company’s needs. For instance, cloud native AI services make it simple to grow and integrate with new technologies.
5.8 Foster cross functional collaboration
Integration of AI is more than just an IT project. Business units, data scientists, compliance teams, and end users must all contribute. Collaboration increases adoption and effectiveness by ensuring that AI solutions are in line with business objectives and technical specifications.
Organizations can turn AI integration from a risky experiment into a planned, effective modernization strategy by adhering to these practices.
6.How to Select the Right AI Tools for Legacy Systems
6.1 Evaluate compatibility with existing infrastructure
The ideal AI tool should blend in perfectly with the existing setting. Seek out solutions that support connectors designed for older platforms, common protocols, and APIs.
6.2 Consider customization and flexibility
The configurations of legacy systems are frequently distinct. Rigid, one size fits all solutions will not be as useful as AI tools that enable customization, such as tailoring models to particular workflows.
6.3 Look for proven enterprise use cases
Select suppliers who have demonstrated deployments in related industries and case studies. For instance, a bank assessing AI fraud detection ought to favor solutions with a proven track record in financial services.
6.4 Assess vendor support and long term viability
Integration of AI requires sustained effort. Vendors ought to provide a clear roadmap, frequent updates, and robust technical support. It’s risky to work with a vendor who might disappear in a few years.
Consider choosing AI tools as a long term companion rather than merely a temporary solution.
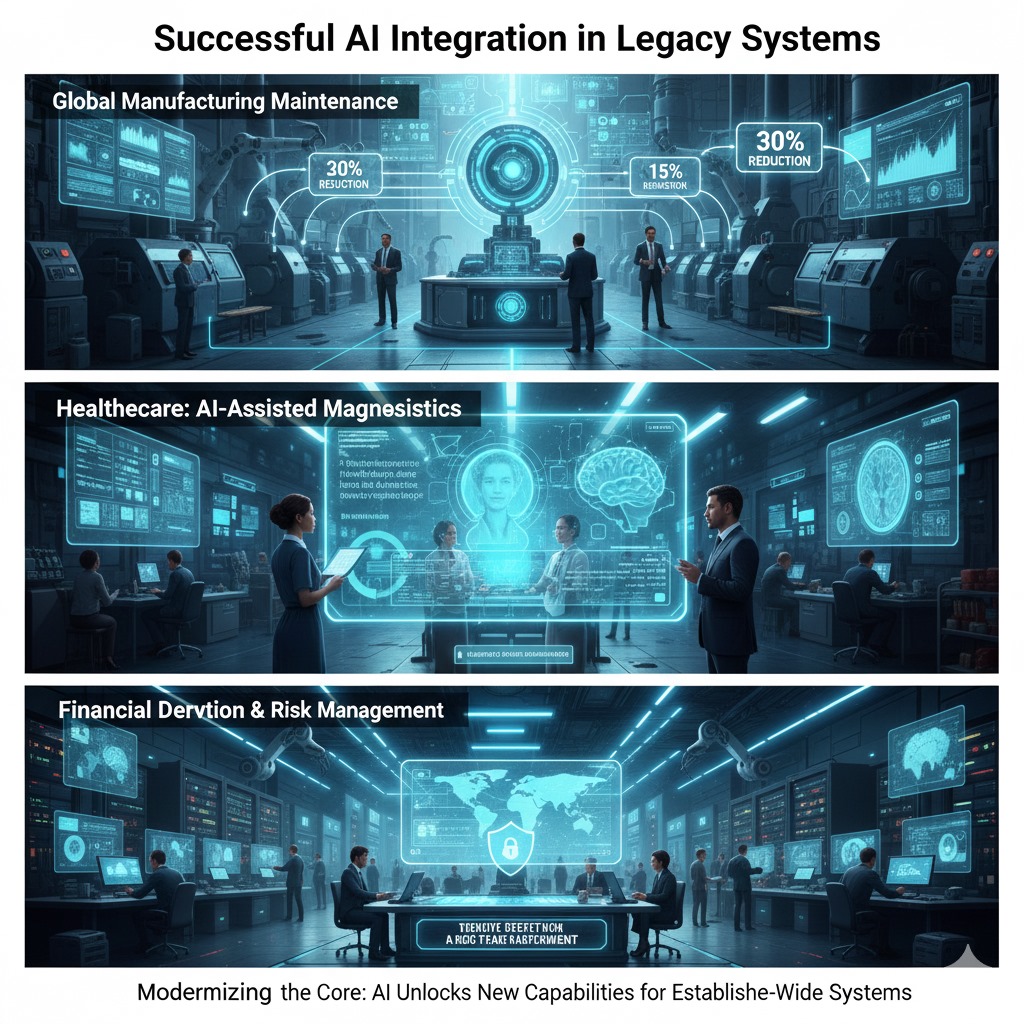
7.Case Studies: Successful AI Integration in Legacy Systems
Manufacturing: predictive maintenance
A multinational manufacturer used equipment systems that were decades old. The business was able to anticipate failures before they occurred by layering AI powered predictive maintenance tools. This prolonged the life of machinery without requiring a system overhaul and decreased downtime by thirty percent.
Healthcare: AI assisted diagnostics
Legacy electronic health record (EHR) systems are frequently used in hospitals. AI diagnostic tools that examined imaging data and patient histories were incorporated by one healthcare provider. The AI enhanced patient outcomes by lowering treatment time and improving diagnostic accuracy despite utilizing outdated infrastructure.
Banking: fraud detection and risk management
A legacy mainframe was used by a traditional bank to process transactions. The bank was able to detect suspicious activity in real time by incorporating AI fraud detection algorithms.
In spite of its reliance on outdated systems, this enhanced security and increased customer trust, presenting the bank as progressive.
8.Common Mistakes to Avoid
Ignoring change management
Integration may stall if organizational and cultural resistance are not addressed. To adopt new tools, employees require involvement, training, and assurance.
Relying solely on vendor promises
Capabilities may be oversold by vendors. Organizations run the risk of investing in ineffective tools if they don’t conduct independent evaluation and pilot testing.
Underestimating data preparation needs
Poor data quality is a common reason why AI projects fail. Integration efforts may be derailed if data cleaning and structuring are neglected.
Failing to plan for scalability
AI ought to develop alongside the industry. Rework is expensive when solutions are implemented without taking future demands into account.
By avoiding these traps, AI integration initiatives are guaranteed to produce the desired outcomes.
Read more: ‘Modernizing legacy IT systems with n8n, Agents & MCP …
9.Future Trends in AI and Legacy System Modernization
Rise of AI driven automation platforms
AI powered automation platforms that work directly with legacy systems will become more and more popular in organizations. By managing repetitive tasks, these platforms serve as “digital coworkers,” freeing up staff members for more valuable work.
Increased use of hybrid cloud and edge computing
While AI workloads operate in the cloud, hybrid cloud models will enable legacy systems to maintain essential features. In contrast, edge computing improves performance in sectors like manufacturing and healthcare by bringing AI closer to data sources.
Read more: Integration of AI into Traditional Systems // Hakan Tek …
Integration of generative AI for decision support
Beyond chatbots, generative AI will advance to facilitate sophisticated decision making. For example, it could use legacy data to simulate business scenarios, giving leaders useful insights.
In the future, legacy systems will be evolved through AI driven modernization rather than being completely replaced.
10.Conclusion
Building intelligent extensions is more important when integrating AI tools into legacy systems than dismantling outdated foundations. Organizations can achieve new levels of productivity, intelligence, and competitiveness by carefully addressing obstacles, adhering to best practices, and choosing the appropriate tools. By bridging the gap between stability and innovation, successful integration demonstrates how AI can transform outdated systems into potent engines for the future.
Read more: Can AI Reduce Traffic in Big Cities? 7 Shocking Ways
11.Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are the main benefits of adding AI to legacy systems?
Key benefits include improved efficiency, cost savings, better decision making, and maintaining competitiveness without replacing core infrastructure.
2. Can AI work with outdated programming languages and platforms?
Yes. APIs, middleware, and specialized integration tools allow AI to interact with legacy systems written in older languages like COBOL.
3. How do organizations minimize disruption during integration?
Start with pilot projects, implement changes gradually, and maintain clear communication with stakeholders. This reduces risks and downtime.
4. What role does cloud technology play in AI integration?
Cloud platforms provide scalable, flexible environments for running AI workloads, making integration with legacy systems smoother and more cost effective.
5. Is AI integration cost effective for mid sized enterprises?
While initial costs may be high, long term benefits such as reduced maintenance, automation, and improved decision making often outweigh investments.
6. How long does a typical AI integration project take?
Timelines vary but typically range from a few months for small pilots to one or two years for enterprise-wide rollouts.
7. Which industries benefit the most from AI enabled legacy systems?
Industries like manufacturing, healthcare, and finance benefit greatly due to their reliance on data heavy processes and need for efficiency.
8. How can organizations ensure AI integration is secure and compliant?
Adopt modern security practices, conduct regular audits, and align integration efforts with relevant regulations and compliance frameworks.
9. What skills are required for teams managing AI enabled legacy systems?
Skills include data engineering, AI/ML expertise, cybersecurity, and strong project management. Cross functional collaboration is also critical.
10. Will AI eventually replace legacy systems altogether?
Over time, some legacy systems may be phased out. However, many organizations will continue to extend their lifespan by layering AI on top, creating hybrid environments.

