Introduction
Healthcare is rapidly changing due to artificial intelligence (AI). AI is taking on tasks that were previously performed by physicians, such as interpreting medical scans and forecasting diseases. However, the crucial question still stands: will AI only serve as a potent tool in the hands of human doctors, or can it actually replace them?
What is AI in Healthcare?
In the context of healthcare, artificial intelligence refers to the application of computer systems that can “learn,” analyze, and make decisions in a manner similar to that of the human brain, but frequently more quickly. AI systems analyze vast volumes of medical data to find trends, forecast results, and recommend treatments rather than depending on intuition or memory.
An AI system, for instance, can analyze thousands of X-rays in a matter of seconds and identify possible tumors more reliably than a weary radiologist at the end of a long shift. Similar to medical chatbots, virtual assistants can respond to inquiries from patients regarding symptoms or prescription drugs. AI powered predictive analytics tools can identify patients who are at a higher risk of developing diseases like diabetes or heart disease.
Consider AI as an enhanced assistant. Although it can swiftly analyze data that could take years for a human to sort through, it cannot take the place of human curiosity or compassion. In the same way that calculators helped mathematicians solve more complex problems rather than eradicate them, artificial intelligence is poised to do the same in the medical field.
How AI is Currently Used in Medicine
Diagnostic Imaging and Pattern Recognition
AI systems are very good at identifying patterns in pictures. AI tools can identify minute anomalies in X-rays, MRIs, CT scans, or skin photos in radiology, dermatology, and pathology. Some AI systems, for instance, are able to identify early indicators of diabetic eye disease or lung cancer before human physicians would typically do so.
Virtual Health Assistants and Chatbots
Digital assistants and chatbots assist patients with scheduling appointments, responding to inquiries, and guiding them through the healing process. By offering prompt answers to common issues, these tools lessen the workload for physicians and nurses and increase access to healthcare.
Predictive Analytics for Treatment Planning
AI is used by hospitals to forecast patient outcomes. For example, algorithms can predict who may be more susceptible to complications by analyzing lab results, lifestyle choices, and medical histories. This increases patient safety by enabling medical professionals to act sooner.
Robotic Surgery and Automation
AI-guided robotic surgery enables more accurate procedures with smaller incisions, faster recovery times, and fewer mistakes. In the meantime, automation is being used to reduce human error and save time in jobs like lab work and drug dispensing.
To put it briefly, AI is already deeply ingrained in many facets of medicine, supporting improved care in the background.
Benefits of AI in Healthcare
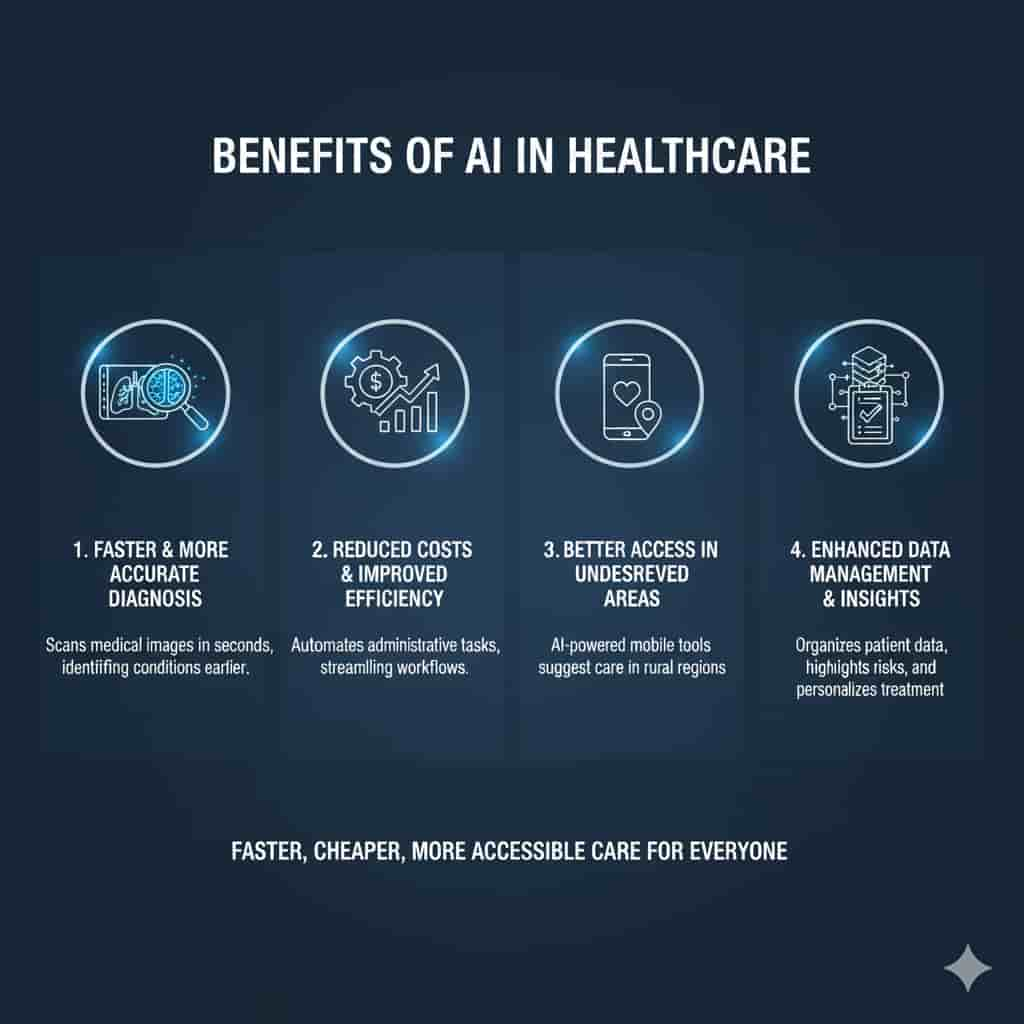
1. Faster and More Accurate Diagnosis
AI can identify conditions before human doctors by quickly scanning through test results or medical images. This speed may allow for the early detection of a potentially fatal illness.
2. Reduced Costs and Improved Efficiency
AI helps hospitals expedite administrative tasks, such as scheduling surgeries and processing insurance claims. Healthcare providers can focus on patients instead of paperwork by automating repetitive tasks, which will ultimately lower costs.
3. Better Access in Underserved Areas
AI powered tools can help in low income or rural areas where doctors are hard to come by. Mobile apps, for example, can evaluate a picture of a rash or cough symptoms and recommend whether the patient needs to go to the emergency room.
4. Enhanced Data Management and Insights
Physicians handle enormous volumes of patient data. AI systems are capable of organizing this data, highlighting important risks, and even suggesting individualized treatment regimens.
These advantages imply that AI may speed up, lower the cost of, and increase access to healthcare an alluring prospect in a society where many people find it difficult to receive high quality care.
Limitations of AI in Healthcare
1. Lack of Empathy and Human Touch
AI is unable to offer compassion, consolation, or emotional support qualities that many patients find most important during trying times. A machine cannot hold a patient’s hand or comprehend their fears, but it can explain treatment options.
2. Ethical and Privacy Concerns
Large volumes of patient data are essential to AI systems. Big questions are raised by this. Who owns the data? How safe is it? Is it possible for private health information to be misused?
3. Risk of Errors and Over-Reliance
AI isn’t flawless, even though it can perform better than humans in some tasks. Serious repercussions could result from an AI system misdiagnosing a patient, particularly if medical professionals follow its recommendations without question.
4. High Costs of Implementation
It is costly to install AI systems, train employees, and maintain technology. A disparity between wealthy and resource poor healthcare facilities could result from smaller hospitals’ inability to purchase these instruments.
These restrictions serve as a reminder that AI is a tool with both advantages and disadvantages rather than a miracle cure.
Will AI Replace Doctors or Assist Them?
This is the main point of contention. Let’s examine both perspectives.
The Case for Replacement
In some tasks, like analyzing medical scans, processing data, or forecasting disease risks, AI already outperforms humans. Machines are not emotionally biased, fatigued, or distracted. Theoretically, this could mean that doctors won’t be needed for some administrative and diagnostic duties in the future.
The Case for Assistance
However, being a doctor involves more than just math. When making treatment decisions, doctors consider personal values, foster trust, and provide comfort to their patients. These human characteristics cannot be replaced. A human physician must consider the patient’s life, preferences, and emotional state when interpreting any recommendations made by AI.
Future Outlook
The future is probably going to be one of collaboration rather than replacement. Similar to how pilots use autopilot systems, doctors will collaborate with AI. The human pilot is still necessary for judgment, decision making, and emergencies even though autopilot can handle the majority of the flying.
Similarly, while doctors concentrate on empathy, communication, and moral decision making, AI might take care of the labor-intensive data analysis. To put it another way, AI will give doctors superpowers rather than replace them.
How AI Could Change the Doctor Patient Relationship
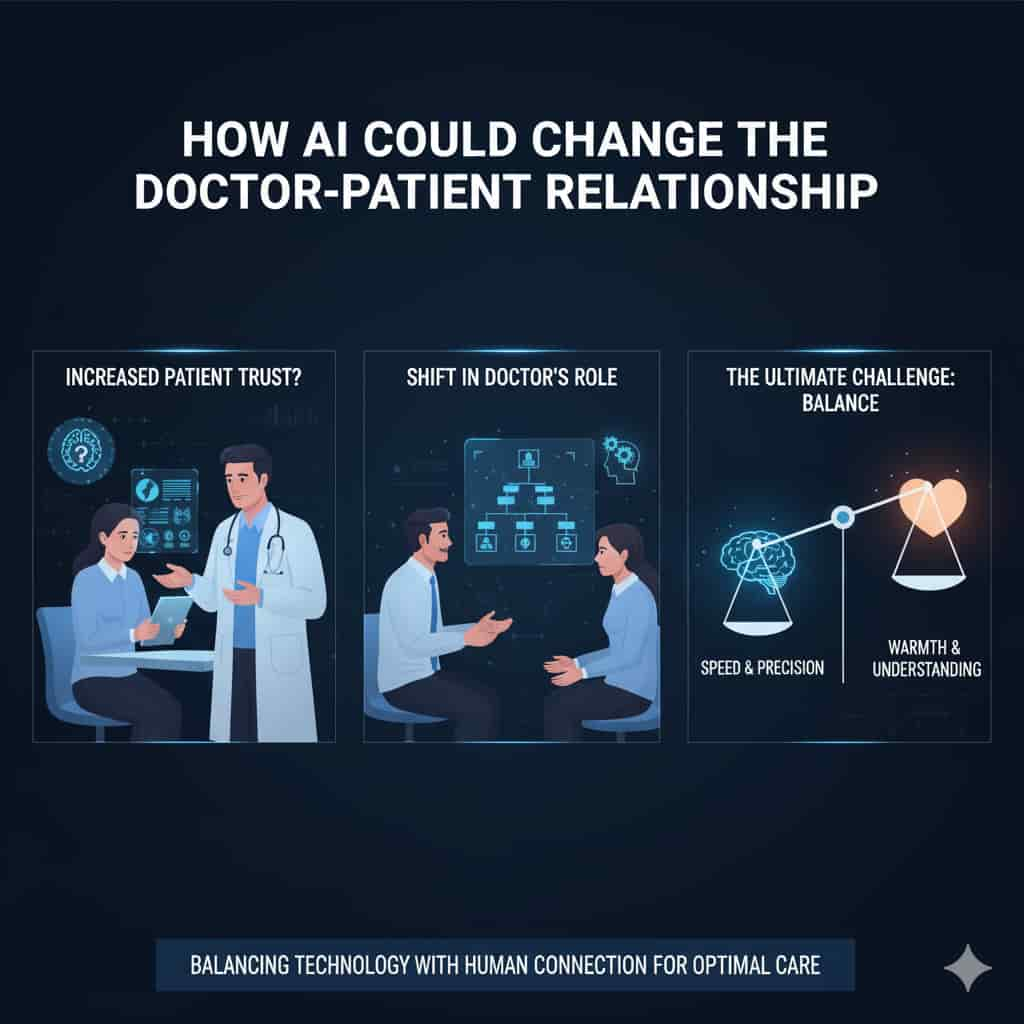
The doctor-patient relationship will unavoidably change as AI enters the examination room.
If AI consistently produces accurate results, patients may start to trust AI tools as much as they trust physicians. However, this could also lead to conflict, who does the patient trust if a doctor recommends a different course of action and an AI suggests a different one?
Additionally, doctors might spend more time helping patients make decisions rather than diagnosing. This change may allow more time for in depth discussions, but if technology takes center stage, it may also depersonalize care.
In the end, the difficulty will be striking a balance between AI’s speed and accuracy and human warmth and comprehension.
Ethical and Legal Challenges
1. Accountability in Case of Misdiagnosis
Who is in charge if an AI system makes the incorrect diagnosis? Who trusted the tool the doctor, the hospital, or the software developer? This is a gray area because there are currently no clear laws.
2. Patient Data Security and Privacy
Data is essential to AI, but sharing and storing health information makes it vulnerable to hacking or abuse. Maintaining patient trust requires making sure that systems are private and secure.
3. Bias and Fairness in AI Systems
AI learns from data, but the system may produce unfair or erroneous results if the data contains biases (such as underrepresentation of particular ethnic groups). For AI to be safe for everyone, these biases must be addressed.
AI will continue to be a double-edged sword in medicine until these moral and legal issues are resolved.
Read more: AI is Coming for Every Medical Specialty (Yes, Even Yours)
What the Future of Medicine Might Look Like
In terms of the future of medicine, cooperation appears to be more likely than replacement.
We might witness “hybrid care” in the next ten to twenty years, where medical professionals collaborate with AI technologies. For instance, a patient may upload symptoms to an app that creates an initial report, which the physician then examines and customizes.
With AI enabling virtual examinations for patients in remote areas, remote care will also grow. It will become commonplace to customize treatments based on lifestyle, genetics, and AI driven insights.
Although their roles may change, doctors will still play a crucial role in healthcare. They will put more of an emphasis on patient communication, empathy, and moral decision making rather than devoting hours to data analysis.
In short, the stethoscope of tomorrow may be powered by AI, but the heart of medicine will remain human.
Read more: How AI Personalized Learning for Each Student? Best in 2025
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can AI make medical decisions on its own?
Not entirely. AI can suggest diagnoses or treatments, but final decisions are usually made by doctors who consider the patient’s overall situation.
2. Are AI diagnoses more accurate than doctors?
In some areas, like image analysis, AI can match or even surpass human accuracy. But it lacks the full context and judgment that doctors bring to the table.
3. Will patients trust AI doctors?
Trust will depend on transparency and proven results. Many patients may trust AI for second opinions but still prefer human doctors for final decisions.
4. How secure is my health data with AI systems?
Security depends on the safeguards in place. Leading healthcare providers use encryption and strict privacy rules, but no system is 100% immune to breaches.
5. What jobs in healthcare are most at risk from AI?
Administrative roles, such as billing or scheduling, are most at risk. Doctors and nurses, who provide human interaction, are less likely to be replaced.
6. Will AI reduce the cost of healthcare?
Potentially. By streamlining processes and reducing errors, AI can lower costs, but the initial investment is high.
7. How do doctors feel about AI in medicine?
Reactions are mixed. Some see it as a helpful tool, while others worry it could reduce their autonomy or overwhelm them with new responsibilities.
8. What role will human empathy play in future healthcare?
Empathy will remain irreplaceable. Patients don’t just want answers they want understanding, comfort, and reassurance that only humans can provide.
Read more: Is AI transforming the future of healthcare? | The Stream
Final Thought
So, can AI replace doctors? The short answer is not entirely. AI is powerful, but it lacks the empathy, ethics, and human judgment that define good medicine. Instead of replacing doctors, AI is more likely to become their most valuable partner one that makes healthcare smarter, faster, and more accessible for everyone.

